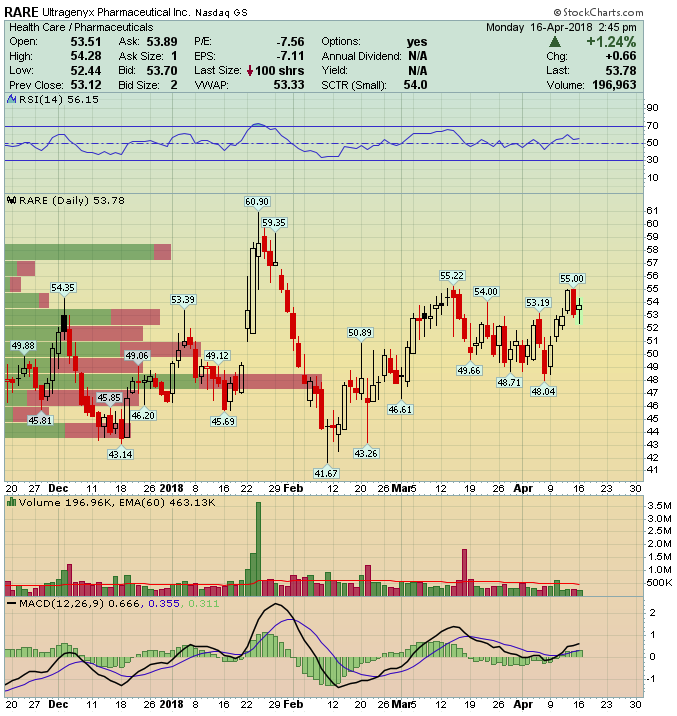
Ultragenyx Pharmaceutical (RARE) – Catalyst Rich 2018
Ultragenyx Pharmaceutical Inc (RARE) is a clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company focused on the development and commercialization of treatments for genetic diseases.
Its clinical-stage pipeline consists of two product categories: biologics, and small-molecule substrate replacement therapies. The company is headquartered in Novato California, just north of San Francisco and runs clinical studies on wholly-owned therapies or under license from other biopharmaceutical firms.
2018 Catalysts
Ultragenyx’ 2018 calendar is filled with possible catalyst dates, all outlined below and then separately discussed.
- FDA PDUFA decision on XLH on April 17th 2018
- Phase III data in Pediatric XLH in 2H2018
- Phase II data in TIO in 1H2018
- Updates on LC-FAOD by mid-2018
- Phase III data on GLUT1 DS in 2H2018
- Early-stage clinical data on DTX301 and DTX401 in 2H2018
Burosumab (KRN23)
Burosumab is a treatment targeted for X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH) and tumor-induced osteomalacia (TIO). Studies are being conducted in collaboration with Japanese pharmaceutical company Kyowa Hakko Kirin.
X-Linked Hypophosphatemia (XLH)
XLH is a disease typically diagnosed in childhood and is the result of phosphate wasting in the kidneys. This lowers levels of phosphate in the blood and in turn leads to inappropriately low serum 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D (the active form of vitamin D) levels causing softening of the bones. When the condition occurs in childhood, it is known as rickets and precipitates obvious skeletal deformities. In adults, it is called osteomalacia.
Clinical data showed that at the 24-week interval, the therapy outperformed placebo in regulating serum phosphorus levels, and also improved clinical symptoms of XLH. After the initial 24-week time frame, patients receiving the placebo were administered Burosumab for a 24-week period as well with 89% of subjects showing similar improved phosphorus levels as the first group’s 84%. Longer-term data has shown symptomatic improvements and also the ability to promote bone healing in adult patients. A decrease in pain medication requirement was also noted with Burosumab usage.
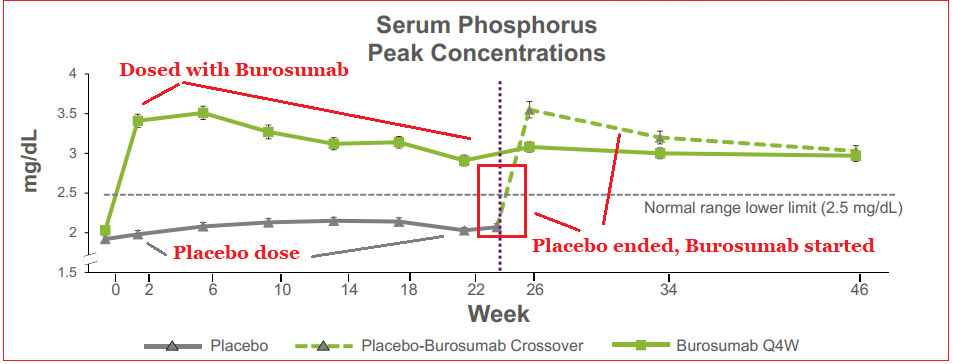
The FDA had previously designated Burosumab as a Breakthrough Therapy, granting it priority review based on guideline criteria, including high-quality evidence of treatment efficacy. As well, the FDA announced that there would not be an Advisory Committee panel meeting which could mean that the strength of the data negates further scrutiny.
A separate pediatric-specific trial is also being conducted with Phase III data expected in 2H2018.
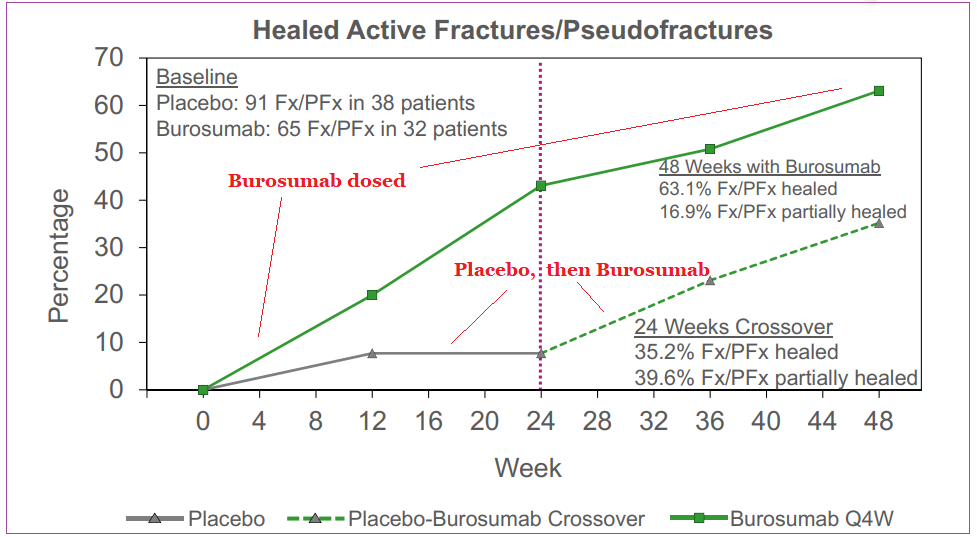
Tumor-Induced Osteomalacia (TIO)
Burosumab’s second indication trials target TIO, a disease characterized by benign tumors producing excess levels of FGF23 hormone that reduces serum levels of phosphorous and vitamin D. Resultant tumors from this condition that cannot be resected (partially or totally removed) are treated with phosphate and/or vitamin D replacement therapies which have limited efficiency as they do not treat the underlying disease.
Ultragenyx’ application of Burosumab in this instance is designed to inhibit excessive activity of the hormone by bonding to it, leading to restored normal phosphate reabsorption.
In early 2016, positive Interim Phase II data from the first eight patients was announced, showing improvements in both serum phosphate levels and associated bone metabolism.
UX007
An investigational, pharmaceutical-grade, specially designed synthetic triglyceride compound which Ultragenyx is developing for tow applications of different disorders caused by genetic defects, neither of which has a current FDA-approved treatment, with both typically treated by specific diets. Ultragenyx has licensed rights to UX007 from Baylor Research Institute.
Long-chain Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders (LC-FAOD)
The first UX007 trial is for a disorder that prevents the body from converting fat to energy, a condition that can lead to severe depletion of glucose and result in serious heart, liver and muscle disease bringing on early death.
Current therapy includes specific diets and medium-chain triglyceride oil, however many patients continue to experience significant metabolic issues requiring hospitalization. UX007 therapy is intended to bypass the genetic block that prevents normal fatty acid metabolism, producing subtrates (molecules) that improve energy production in patients.

Phase II trial results showed very encouraging 48.1% reduction in major clinical events after 78 weeks (18 months) of treatment when compared to the 18 months preceding the therapy. These results are strong enough to bring a possible NDA filing just on Phase II data outcome, expected in mid-2018.
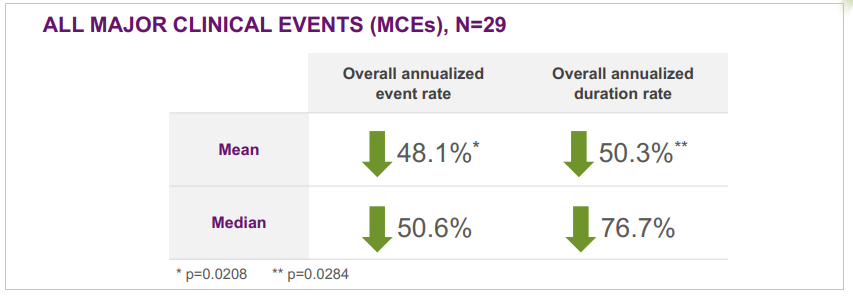
Glucose Transporter Type 1 Deficiency Syndrome (GLUT1 DS)
The second indication is for a severely debilitating disease leading to seizures, development delay and movement disorders caused by a genetic defect resulting in abnormal transport of glucose to the brain: glucose is the brain’s main source of fuel and inadequate levels manifest in epileptic seizures. Physical symptoms include microcephaly, a condition where the circumference of the head is smaller than normal for the patient’s age and size.
In this application, UX007 is metabolized into heptanoate, a fatty acid which is able to cross the blood-brain barrier and provide energy to the brain.

DTX301
In early March, Ultragenyx announced positive Phase I/II long-term safety and efficacy data in an investigational gene therapy for the treatment of Ornithine Transcarbamylase Deficiency (OTC), an inherited disorder that results in ammonia accumulation in the blood, with high levels causing toxicity to the nervous system. The only current curative approach is liver transplantation.
The first dose cohort was a small study on three patients lasting 52 weeks. The first patient to receive treatment showed normalized ureagenesis (detoxification of ammonia from the blood) levels that substantially increased over 24 weeks. At the time of this update, the other two patients hadn’t shown a clinically meaningful change in ureagenesis rate at week 20 and 12 respectively.
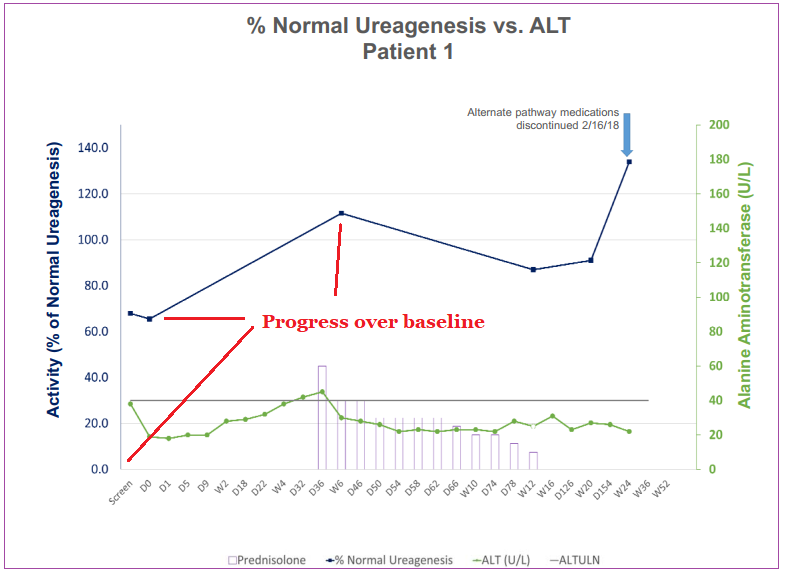
None of the three patients involved in the trial had any neither infusion-related nor serious adverse events and any events that did occur were low-Grade ½ which were resolved successfully.
DTX301 was granted Orphan Drug Designation in both the United States and Europe. Trials will now proceed to the second, higher-dose cohort of the study as the Data Monitoring Committee has completed its review of the first group.
DTX401
Another investigational-stage therapy in its early stages of development, DTX401 targets Glycogen Storage Disease Type 1a (GSD1a), an inherited disorder caused by the buildup of glycogen in the body’s cells, impairing certain organs, especially the liver and kidneys from performing normal functions.
Symptoms for GSD1a typically show at around 3-4 months of age and result in low blood-sugar leading to seizures. Physically, afflicted children are short of stature with thin arms and legs, additionally an enlarged liver may cause a protruding abdomen.
Both DTX301 and DTX401 became property of Ultragenyx after it acquired Dimension Therapeutics in November 2017 for $151M.
ClosingThoughts
Ultragenyx has multiple catalysts over the course of 2018 and plenty of funds to continue its research without a secondary offering; the company exited 2017 with $235M in cash and short-term investments versus $71M in liabilities of which $61M were accrued expenses. It recently sold a Priority Review Voucher for $130M and should receive another upon Burosumab approval. Encouraging data from ongoing trials could pave the way for the next set of positive results that may drive shares higher this year.